# A Better Camera
I've been putting this off for a while. Implementing a camera isn't specifically related to using WGPU properly, but it's been bugging me, so let's do it.
lib.rs is getting a little crowded, so let's create a camera.rs file to put our camera code. The first things we're going to put in it are some imports and our OPENGL_TO_WGPU_MATRIX.
use cgmath::*;
use winit::event::*;
use winit::dpi::PhysicalPosition;
use instant::Duration;
use std::f32::consts::FRAC_PI_2;
#[rustfmt::skip]
pub const OPENGL_TO_WGPU_MATRIX: cgmath::Matrix4<f32> = cgmath::Matrix4::from_cols(
cgmath::Vector4::new(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
cgmath::Vector4::new(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0),
cgmath::Vector4::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0),
cgmath::Vector4::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0),
);
const SAFE_FRAC_PI_2: f32 = FRAC_PI_2 - 0.0001;
std::time::Instant panics on WASM, so we'll use the instant crate (opens new window). You'll want to include it in your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
# ...
instant = "0.1"
[target.'cfg(target_arch = "wasm32")'.dependencies]
instant = { version = "0.1", features = [ "wasm-bindgen" ] }
# The Camera
Next, we need to create a new Camera struct. We're going to be using an FPS-style camera, so we'll store the position and the yaw (horizontal rotation), and pitch (vertical rotation). We'll have a calc_matrix method to create our view matrix.
#[derive(Debug)]
pub struct Camera {
pub position: Point3<f32>,
yaw: Rad<f32>,
pitch: Rad<f32>,
}
impl Camera {
pub fn new<
V: Into<Point3<f32>>,
Y: Into<Rad<f32>>,
P: Into<Rad<f32>>,
>(
position: V,
yaw: Y,
pitch: P,
) -> Self {
Self {
position: position.into(),
yaw: yaw.into(),
pitch: pitch.into(),
}
}
pub fn calc_matrix(&self) -> Matrix4<f32> {
let (sin_pitch, cos_pitch) = self.pitch.0.sin_cos();
let (sin_yaw, cos_yaw) = self.yaw.0.sin_cos();
Matrix4::look_to_rh(
self.position,
Vector3::new(
cos_pitch * cos_yaw,
sin_pitch,
cos_pitch * sin_yaw
).normalize(),
Vector3::unit_y(),
)
}
}
# The Projection
I've decided to split the projection from the camera. The projection only needs to change if the window resizes, so let's create a Projection struct.
pub struct Projection {
aspect: f32,
fovy: Rad<f32>,
znear: f32,
zfar: f32,
}
impl Projection {
pub fn new<F: Into<Rad<f32>>>(
width: u32,
height: u32,
fovy: F,
znear: f32,
zfar: f32,
) -> Self {
Self {
aspect: width as f32 / height as f32,
fovy: fovy.into(),
znear,
zfar,
}
}
pub fn resize(&mut self, width: u32, height: u32) {
self.aspect = width as f32 / height as f32;
}
pub fn calc_matrix(&self) -> Matrix4<f32> {
OPENGL_TO_WGPU_MATRIX * perspective(self.fovy, self.aspect, self.znear, self.zfar)
}
}
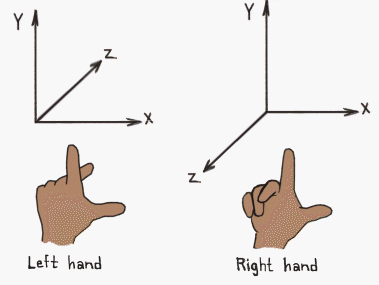
One thing to note: cgmath currently returns a right-handed projection matrix from the perspective function. This means that the z-axis points out of the screen. If you want the z-axis to be into the screen (aka. a left-handed projection matrix), you'll have to code your own.
You can tell the difference between a right-handed coordinate system and a left-handed one by using your hands. Point your thumb to the right. This is the x-axis. Point your pointer finger up. This is the y-axis. Extend your middle finger. This is the z-axis. On your right hand, your middle finger should be pointing towards you. On your left hand, it should be pointing away.
# The Camera Controller
Our camera is different, so we'll need a new camera controller. Add the following to camera.rs.
#[derive(Debug)]
pub struct CameraController {
amount_left: f32,
amount_right: f32,
amount_forward: f32,
amount_backward: f32,
amount_up: f32,
amount_down: f32,
rotate_horizontal: f32,
rotate_vertical: f32,
scroll: f32,
speed: f32,
sensitivity: f32,
}
impl CameraController {
pub fn new(speed: f32, sensitivity: f32) -> Self {
Self {
amount_left: 0.0,
amount_right: 0.0,
amount_forward: 0.0,
amount_backward: 0.0,
amount_up: 0.0,
amount_down: 0.0,
rotate_horizontal: 0.0,
rotate_vertical: 0.0,
scroll: 0.0,
speed,
sensitivity,
}
}
pub fn process_keyboard(&mut self, key: VirtualKeyCode, state: ElementState) -> bool{
let amount = if state == ElementState::Pressed { 1.0 } else { 0.0 };
match key {
VirtualKeyCode::W | VirtualKeyCode::Up => {
self.amount_forward = amount;
true
}
VirtualKeyCode::S | VirtualKeyCode::Down => {
self.amount_backward = amount;
true
}
VirtualKeyCode::A | VirtualKeyCode::Left => {
self.amount_left = amount;
true
}
VirtualKeyCode::D | VirtualKeyCode::Right => {
self.amount_right = amount;
true
}
VirtualKeyCode::Space => {
self.amount_up = amount;
true
}
VirtualKeyCode::LShift => {
self.amount_down = amount;
true
}
_ => false,
}
}
pub fn handle_mouse(&mut self, mouse_dx: f64, mouse_dy: f64) {
self.rotate_horizontal = mouse_dx as f32;
self.rotate_vertical = mouse_dy as f32;
}
pub fn handle_mouse_scroll(&mut self, delta: &MouseScrollDelta) {
self.scroll = -match delta {
// I'm assuming a line is about 100 pixels
MouseScrollDelta::LineDelta(_, scroll) => scroll * 100.0,
MouseScrollDelta::PixelDelta(PhysicalPosition {
y: scroll,
..
}) => *scroll as f32,
};
}
pub fn update_camera(&mut self, camera: &mut Camera, dt: Duration) {
let dt = dt.as_secs_f32();
// Move forward/backward and left/right
let (yaw_sin, yaw_cos) = camera.yaw.0.sin_cos();
let forward = Vector3::new(yaw_cos, 0.0, yaw_sin).normalize();
let right = Vector3::new(-yaw_sin, 0.0, yaw_cos).normalize();
camera.position += forward * (self.amount_forward - self.amount_backward) * self.speed * dt;
camera.position += right * (self.amount_right - self.amount_left) * self.speed * dt;
// Move in/out (aka. "zoom")
// Note: this isn't an actual zoom. The camera's position
// changes when zooming. I've added this to make it easier
// to get closer to an object you want to focus on.
let (pitch_sin, pitch_cos) = camera.pitch.0.sin_cos();
let scrollward = Vector3::new(pitch_cos * yaw_cos, pitch_sin, pitch_cos * yaw_sin).normalize();
camera.position += scrollward * self.scroll * self.speed * self.sensitivity * dt;
self.scroll = 0.0;
// Move up/down. Since we don't use roll, we can just
// modify the y coordinate directly.
camera.position.y += (self.amount_up - self.amount_down) * self.speed * dt;
// Rotate
camera.yaw += Rad(self.rotate_horizontal) * self.sensitivity * dt;
camera.pitch += Rad(-self.rotate_vertical) * self.sensitivity * dt;
// If process_mouse isn't called every frame, these values
// will not get set to zero, and the camera will rotate
// when moving in a non-cardinal direction.
self.rotate_horizontal = 0.0;
self.rotate_vertical = 0.0;
// Keep the camera's angle from going too high/low.
if camera.pitch < -Rad(SAFE_FRAC_PI_2) {
camera.pitch = -Rad(SAFE_FRAC_PI_2);
} else if camera.pitch > Rad(SAFE_FRAC_PI_2) {
camera.pitch = Rad(SAFE_FRAC_PI_2);
}
}
}
# Cleaning up lib.rs
First things first, we need to delete Camera and CameraController, as well as the extra OPENGL_TO_WGPU_MATRIX from lib.rs. Once you've done that, import camera.rs.
mod model;
mod texture;
mod camera; // NEW!
We need to update update_view_proj to use our new Camera and Projection.
impl CameraUniform {
// ...
// UPDATED!
fn update_view_proj(&mut self, camera: &camera::Camera, projection: &camera::Projection) {
self.view_position = camera.position.to_homogeneous().into();
self.view_proj = (projection.calc_matrix() * camera.calc_matrix()).into();
}
}
We need to change our State to use our Camera, CameraProjection and Projection as well. We'll also add a mouse_pressed field to store whether the mouse was pressed.
pub struct State {
// ...
camera: camera::Camera, // UPDATED!
projection: camera::Projection, // NEW!
camera_controller: camera::CameraController, // UPDATED!
// ...
// NEW!
mouse_pressed: bool,
}
You'll need to import winit::dpi::PhysicalPosition if you haven't already.
We need to update new() as well.
impl State {
async fn new(window: Arc<Window>) -> anyhow::Result<State> {
// ...
// UPDATED!
let camera = camera::Camera::new((0.0, 5.0, 10.0), cgmath::Deg(-90.0), cgmath::Deg(-20.0));
let projection = camera::Projection::new(config.width, config.height, cgmath::Deg(45.0), 0.1, 100.0);
let camera_controller = camera::CameraController::new(4.0, 0.4);
// ...
camera_uniform.update_view_proj(&camera, &projection); // UPDATED!
// ...
Self {
// ...
camera,
projection, // NEW!
camera_controller,
// ...
mouse_pressed: false, // NEW!
}
}
}
We also need to change our projection in resize.
fn resize(&mut self, width: u32, height: u32) {
// UPDATED!
self.projection.resize(width, height);
// ...
}
input() will need to be updated as well. Up to this point, we have been using WindowEvents for our camera controls. While this works, it's not the best solution. The winit docs (opens new window) inform us that OS will often transform the data for the CursorMoved event to allow effects such as cursor acceleration.
Now, to fix this, we could change the input() function to process DeviceEvent instead of WindowEvent, but keyboard and button presses don't get emitted as DeviceEvents on MacOS and WASM. Instead, we'll just remove the CursorMoved check in input() and a manual call to camera_controller.process_mouse() in the run() function.
// UPDATED!
fn input(&mut self, event: &WindowEvent) -> bool {
match event {
WindowEvent::KeyboardInput {
event:
KeyEvent {
physical_key: PhysicalKey::Code(key),
state,
..
},
..
} => self.camera_controller.process_keyboard(*key, *state),
WindowEvent::MouseWheel { delta, .. } => {
self.camera_controller.process_scroll(delta);
true
}
WindowEvent::MouseInput {
button: MouseButton::Left,
state,
..
} => {
self.mouse_pressed = *state == ElementState::Pressed;
true
}
_ => false,
}
}
Here are the changes to run():
fn main() {
// ...
event_loop.run(move |event, control_flow| {
match event {
// ...
// NEW!
Event::DeviceEvent {
event: DeviceEvent::MouseMotion{ delta, },
.. // We're not using device_id currently
} => if state.mouse_pressed {
state.camera_controller.process_mouse(delta.0, delta.1)
}
// UPDATED!
Event::WindowEvent {
ref event,
window_id,
} if window_id == state.window().id() && !state.input(event) => {
match event {
#[cfg(not(target_arch="wasm32"))]
WindowEvent::CloseRequested
| WindowEvent::KeyboardInput {
event:
KeyEvent {
state: ElementState::Pressed,
physical_key: PhysicalKey::Code(KeyCode::Escape),
..
},
..
} => control_flow.exit(),
WindowEvent::Resized(physical_size) => {
state.resize(*physical_size);
}
WindowEvent::ScaleFactorChanged { new_inner_size, .. } => {
state.resize(**new_inner_size);
}
_ => {}
}
}
// ...
}
});
}
The update function requires a bit more explanation. The update_camera function on the CameraController has a parameter dt: Duration, which is the delta time or time between frames. This is to help smooth out the camera movement so that it's not locked by the framerate. Currently, we aren't calculating dt, so I decided to pass it into update as a parameter.
fn update(&mut self, dt: instant::Duration) {
// UPDATED!
self.camera_controller.update_camera(&mut self.camera, dt);
self.camera_uniform.update_view_proj(&self.camera, &self.projection);
// ..
}
While we're at it, let's also use dt for the light's rotation.
self.light_uniform.position =
(cgmath::Quaternion::from_axis_angle((0.0, 1.0, 0.0).into(), cgmath::Deg(60.0 * dt.as_secs_f32()))
* old_position).into(); // UPDATED!
We still need to calculate dt. Let's do that in the main function.
fn main() {
// ...
let mut state = State::new(&window).await;
let mut last_render_time = instant::Instant::now(); // NEW!
event_loop.run(move |event, control_flow| {
match event {
// ...
// UPDATED!
Event::RedrawRequested(window_id) if window_id == state.window().id() => {
let now = instant::Instant::now();
let dt = now - last_render_time;
last_render_time = now;
state.update(dt);
// ...
}
_ => {}
}
});
}
With that, we should be able to move our camera wherever we want.